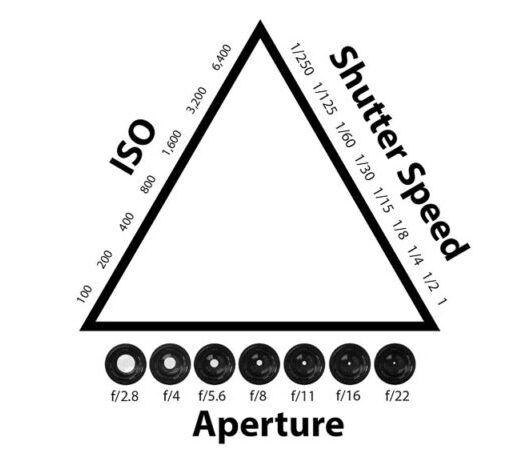
Aperture.
The aperture talks about the hole that the light passes through to get to the film, or the sensor, and is measured in “f stops” which will be what you see on your film camera lenses, or what you will see as a value in the viewfinder or on the back of the screen on your digital camera.
On prime lenses you will generally have a value of between f1.8 going up to f16, or even f22 or f32 on your digital lenses. If you go below F1.8 to f1.4 or f1.2, you have a more expensive lens attached to your camera body. If you can afford it then why not.
The opening or closing of the aperture blades will affect how much of your photo will be in focus and how much “bokeh” you will be able to get for your image. You will hear people talking about depth of field (of view). If I use a large aperture (with a lower f stop number) I will only have a small plane of my image that will be in focus or sharp, and the background will be blurry. My subject will stand out. If I use a smaller aperture (a larger number on the f stop setting), I will have a larger plane of my image that will be.
Application
So this exposure triangle thingy. In the previous sections you have seeen the effects that each element can have on your shot. In photography, as in life, we have to learn how to prioritise. What is the most important for us? How will these settings help us get the photo “we” want and not what the camera thinks “we” want? Do we need to freeze the action? Do we need the creamy bokeh? How much light do we have to play with? What is most important to us? Modern cameras are pretty good with their automatic settings, but when talking about being mindful in photography, it might just be an idea to keep a minimum of control.
Photography with a manual film camera takes this automation away,and brings us back to basics, hence my referring back to them all the time. If you can get well exposed shots with a manual film camera, then using digital is a breeze. In the viewfinder there will be a needle that goes up and down depending on how we change our settings. As I said earlier the ISO value will be chosen by the film you use, and I explained the different values and how they work. So that’s one less thing to worry about. You can’t change your film mid shoot, well you can, but I need a new article to tell you how to do it. So you’re left with aperture and shutter speed controls. There’s no LCD screen with a preview, so you have to become an educated guesser. But if I can, then you can. This needle, or rather a snazzy modern version, will appear in the viewfinder, and you will see it move as you change your setting.
Same tool, just a different format. Or you can cheat, and look at the image preview on the LCD screen. But that’s cheating, and gets you thinking rather than doing.
Always bear in mind that as the light changes, then so will your settings to adjust for this changing light. Just keep an eye on it and be aware as Jean-Claude Van Damme would tell us.
Scenario 1
I need to take photos of little Jimmy’s football match. I need to have a relatively fast shutter speed (about 1/500th of a second with film as my minimum speed, or up to 1/4000th of a second to capture the action with a digital camera), so shutter speed is my priority. That can’t move. So I can play with either my ISO or my aperture to compensate. I would probably take a 400 ISO (or ASA) film because even in sunlight that would allow me to have everything in focus by using f8, or even f16. With digital I can really push up my ISO to around 6400 and not have too much visible noise. The very recent cameras can go even higher without digital noise becoming a problem.
Scenario 2
I want to capture my subject and make the background blurry. Basically bokeh and also low light photography. This could be in street photography, or taking a portrait of somebody where I want the eyes in focus, but not necessarily the ears or back of the head. I will want to use a large aperture (smallest f stop number, so my priority becomes my aperture setting which I don’t want to change. This will give me that creamy bokeh that everyone raves about.But, with a large aperture I’m going to have lots of light hitting my film. I will have to bump up my shutter speed, and lower my ISO by using a slower film like 100 ASA or 200 ASA to compensate.
Scenario 3.
When ambient light is lower, opening up my aperture, lowering my shutter speed I can compensate for this lack of light. I might have to use a tripod if there isn’t enough light, or add a flash to my camera to provide my own light. I could use a higher ISO value and have a film more sensitive to light, but I will get much more grain etc. Everything is about balance and weighing up what “you” want.
Conclusion
Talking about film photography and film speeds etc, was very deliberate on my part. I am convinced that if you can use a manual camera and get good results, then using a digital camera will be so much easier for you.
The exposure triangle is now something that is no longer an enigma. We have talked about the ISO value, the shutter speed, and the aperture, and how these settings will effect your photograph. The ability to master these three elements gives you creative control over your images, allowing you to expose your image the way “you” want to, and you can go back to the articles about composition with a new eye. I want you to enjoy your photography, and you now have the necessary tools and knowledge at your disposal to do so.
I would, as always, urge you to take your camera out and shoot. You can experiment, and practice, and this manual lark will become second nature. You’ve got this!